In this tutorial I will discuss the steps which are necessary to install Exchange 2007 server in Exchange 2003 environment. This solution can be used if you want to migrate from Exchange 2003 to Exchange 2007 and:
- you want to use the current Active Directory
- you want to reuse the existing Exchange environment.
If one of the conditions is not necessary or not possible you should use an other migration scenario, for example a cross-forest migration which can be used to build a new AD parallel to the old AD. This last option is a bit more work then installing an Exchange 2007 server in the current environment.
Before we start you should check a few things:
- which mode is Exchange 2003 currently running ?
- which servicepack is installed for Exchange 2003 ?
These to points can be found out very easy:
- open he system manager and get the properties of the Exchange Organization, look under the section"operation mode" and change it if necessary (WARNING: this action can not be reversed)
- check if SP2 for Exchange 2003 is installed, this can be found under Add/remove programs
An easy tool to check these things is the Exchange Best Practice Analyzer, this tool has an option that can check you existing Exchange environment for Exchange 2007 readiness.
After we did the checks on the Exchange 2003 site we can install Exchange 2007 on a server. Before we start the install ensure that the following components are installed on it:
- install MMC 3.0 (Windows 2003 R2 already has MMC 3.0 in it)
- install .NET 2.0 and the following hotfix, KB 926776
- install Powershell 1.0
- install IIS when your are planning to install the Client Access Role on the same server as the mailbox role server.
When you installed all pre-requisites we can start with installing Exchange 2007. If you have Exchange admin privileges but you can’t create objects in AD because of the rights you have. Ask an administrator who has enough rights to execute the following commands:
- setup /PrepareLegacyExchangePermissions of /PL
- setup /PrepareDomain of /p
You may think I am missing one, this is correct setup /PrepareLegacyExchangePermissions automaticly executes setup /PrepareAD
I will skip the first three steps because you can choose what you want for those. You can for example end logs to Microsoft if it crashes.
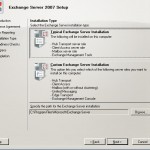
We start with the part where we need to choose which components we like to install.
You have two options here, which one you choose depends on how many servers you have. When you have only one server choose the option Typical Exchange Server Installation this will install the Hub Transport, Client Access, Mailbox Server and Exchange management tools. When you have multiple server then select the option Custom Exchange Server Installation.
When you made a choice press the next button
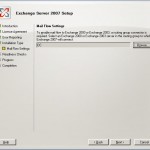
We like to add Exchange 2007 to an existing Exchange 2003 environment, during the setup you need to decide how mail will be send between the Exchange 2003 and Exchange 2007 environment. This will automatically create a separate routing group connector. Via browse you can choose the server, normally this is the Exchange 2003 server which is the bridge-head server, where you would like to create a routing group connector with.
When you have selected the server press next
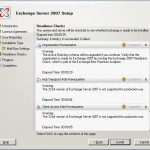
The setup will check if all pre-requisites are met. If there is something wrong/not installed it will give you a warning. When all problems are solved you can continue with the Exchange installation, press next
After waiting a while the setup is ready and you have an Exchange 2007 server in an Exchange 2003 environment.
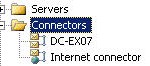
When you start the System Manager from Exchange 2003 and have a look at the connectors you will see the routing group connectorwhich is made during the setup. When you try to modify it you will receive a warning that it can be modified from a Exchange 8.0.30535.0 manager.
During the creation of the routing group connectorthere will be done a few actions more then only creating it. The setup also creates a seperate administrative group and an apart routing group. This two objects are created so that Exchange 2003 and Exchange 2007 can cooperate with each other. In Exchange 2003 you had the possibility to assign delegates per administrative group. In Exchange 2007 there is only one administrative group where all Exchange 2007 servers reside. This group has the following name FYDIBOHF23SPDLT. According to some web page’s this name is created during a cipher has, the original text is EXCHANGE12ROCKS!
Maybe you do now have a question ? Why is there an apart routing group connector created ? Exchange 2003 uses the routing group connector to decide how a mail is delivered to another Exchange Server. In Exchange 2007 this is done by creating separate sites in Active Direcory. The routing group created during installation is calles DWBGZMFD01QNBJR.
All the users that have a mailbox on the Exchange 2007 server need to be administrated via the Exchange Management Console, users who have their mailbox on an Exchange 2003 server need to be administrated from the System Manager.
Moving users from the old server to the new server is not an issue. The only disadvantage of it is that you can’t do it via the GUI, you will have to do it via Powershellmove-mailbox -TargetDatabase “Ex2007 Server\First Storage Group\Mailbox Database -identity UserName
It’s no issue to move mailboxes between Exchange 2003 and Exchange 2007 there is only one remark. Exchange 2007 has an other way of working with “rules” which are created by the clients. The parameter IgnoreRuleLimitErrors can be added to the command to prevent migrating the rules the user created in Outlook, this is only neede when moving a mailbox from Exchange 2007 to Exchange 2000/2003.
This was another tutorial on Exchange 2003, the next tutorial will probably be how to remove the Exchange 2003 server from the environment.